Technical Note 15 – Structural Biology Applications
Structural biology is an important part of Life Science Research focusing on the molecular structure and formation of biological macromolecules ( e.g. proteins, consisting of amino acids, DNA and RNA consisting of nucleotides and cell membranes consisting of lipids). Structural biology is of key interest to biologists as macromolecules perform a majority of cell functions, which are determined primarily by the unique three-dimensional formation of each molecule. This architecture, determined by the “tertiary structure”, depends on the linear sequence considered the “primary structure” of each molecule. The understanding of the tertiary (3D) structure of a molecule is a basic prerequisite for understanding function.
Biological macromolecules are too small to be observed even with the most advanced light based microscopes. In order to visualize the structure of macromolecules, radiation methods with much shorter wavelengths are necessary and for larger molecules even synchrotrons/cyclotron time techniques such as Nucleic Magnetic Resonance (NMR) are required to obtain high enough resolution. In general structural biology investigation methods include:
- Mass spectrometry (MS)
- Macromolecular crystallography (X-ray/XRC)
- Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR)
- Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR)
- Cryogenic Electron Microscopy (cryo-EM)
- Electron crystallography and Microcrystal electron diffraction
- Multiangle light scattering
- Small angle scattering
- Laser absorption spectrometry (LAS)
Typically, all of these methods require highly purified protein samples to provide reliable and reproducible results and to avoid misleading observations and errors caused by potential artifacts and impurities. Accurate quantification is also very important to ensure that enough material is available before applying expensive sample and wasting valuable time and resources in downstream investigations.
The NanoPhotometer® is a unique quality control tool available to scientists that is ideal especially for the analysis of precious protein samples. The patented Sample Compression Technology™ allows measurements with as low as 0.3 µl sample volume and without the need for additional error prone sample preparation steps or expensive consumables. The NanoPhotometer® not only provides independence from the need for surface tension, which protein samples usually lack, but also allows for the measurement of samples containing organic solvents.
Figure 1: Biological Micromoleculas – proteins, DNA/RNA, cell membranes
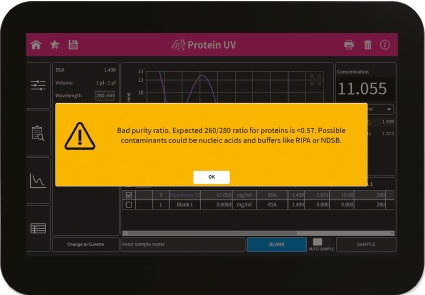
Figure 2: NanoPhotometer® NP80 and a warning screen “Bad purity ratio. Expected 260/280 ratio for proteins is < 0.57. Possible contaminants could be nucleaic acids and buffers like RIPA or NDSB.”
Sample Control™ is an additional feature offering peace of mind for researchers as contaminated samples are flagged and indications are provided on the type of contamination found. For example, nucleic acid residues can be identified by observing the 260/280 nm ratio that the system is automatically detecting and providing the result, with the optimal range being between 0.5 and 0.6 indicating a protein with high purity.
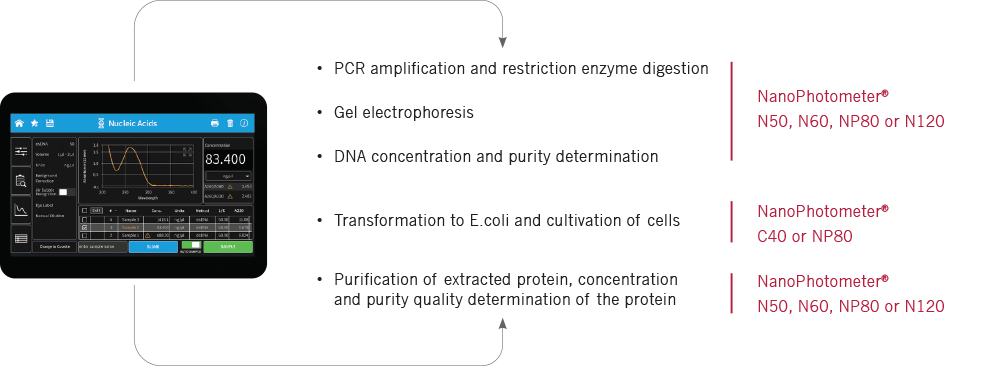
In general, most workflows within structural biology applications start with the production of a protein of interest through expression and its purification. The following diagram shows the wide range of uses for the NanoPhotometer® during the production process:
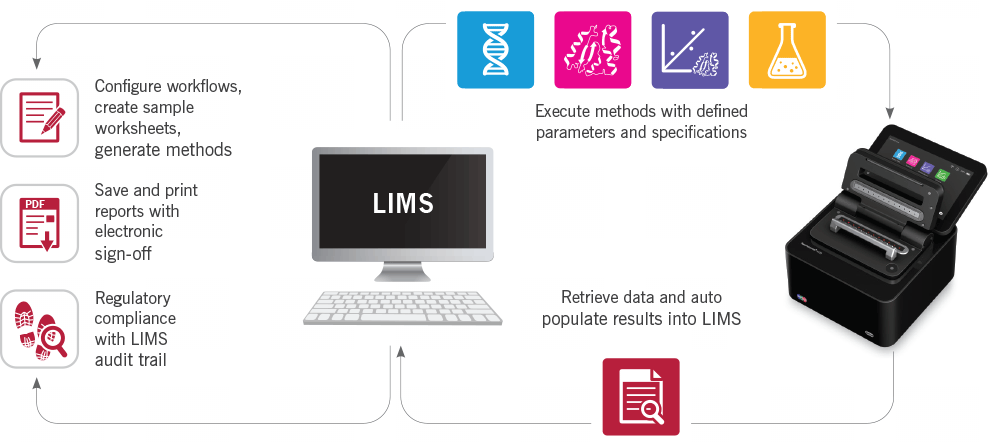
The built-in Web Application Server with REST API allows the easy integration of the NanoPhotometer® into almost any LIMS system. The following flow chart shows the options available to ensure that all data within the entire workflow are constantly monitored and archived automatically. Add more efficiency to your workflow by integrating the NanoPhotometer® with your LIMS to control processes, eliminate errors and save time.
In general, most workflows within structural biology applications start with the production of a protein of interest through expression and its purification. The following diagram shows the wide range of uses for the NanoPhotometer® during the production process:
For further questions or if assistance is needed, please contact your local Implen Support Team at [email protected] or [email protected].