Implen Journal Club
Implen Journal Club
Welcome to the Implen NanoPhotometer® Journal Club. Here we will highlight relevant publications where the Implen NanoPhotometer® helped researchers to unravel the mysteries of modern molecular biology.
Current Month Journal Club Issue
June 2025| Full Newsletter (html) (pdf)
Personalized Medicine at the Push of a Button: 3D-Printed Pills Tailored for You
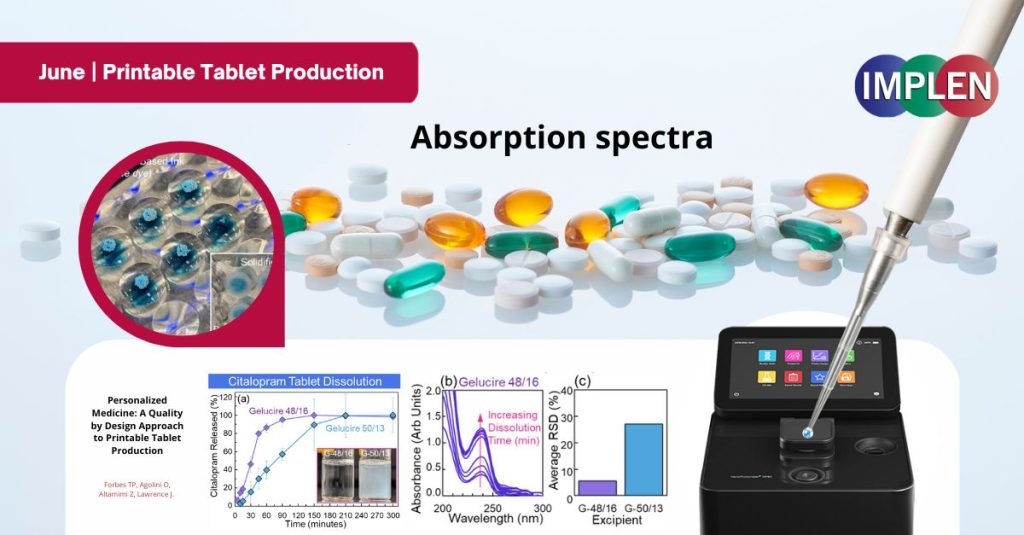
A recent publication in ChemRxiv demonstrated that scientists developed a 3D printing method to make hollow tablets, then filled them with tiny, precise drops of medicine using drop-on-demand inkjet printing. Each pill was tested to ensure the dose was accurate. This method provides the potential for custom medications to be made safely on the spot, giving patients exactly what they need, when they need it.
The Implen NanoPhotometer® was used in this work to collect the absorption spectra of both pharmaceutical ink formulations and manufactured tablets. The spectrophotometer enabled two pathlengths of 0.67 mm (dilution factor 15×) and 0.07 mm (dilution factor 140×). Absorption spectra were collected from 200 nm to 650 nm with nanometer resolution. The compact footprint, approximately 2.5 second analysis, and touchscreen operation provided a standalone format for rapid API ink verification.
#Implen #NanoPhotometer #UV/VIS #Spectroscopy #PersonalizedMedicine #3DPrintedPills #3DPrinting #PointOfCare #PharmaInnovation #PrecisionDosing #CustomMeds #DigitalHealth #PharmaceuticalTech #SmartPharmacy #MedTech #FutureOfMedicine
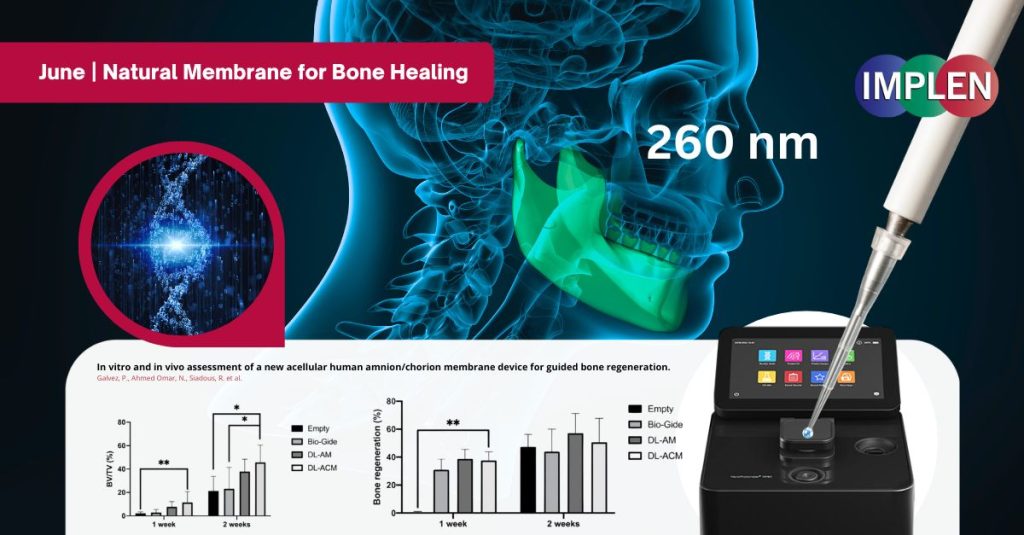
A newly developed natural membrane is making waves in regenerative medicine. It’s thicker, stronger, and easier to handle than previous materials—and it’s showing great promise in helping bones heal faster, especially in dental and jaw surgeries. Backed by rigorous testing and now published in Nature’s Scientific Reports, this innovation could reshape how we approach bone repair.
The Implen NanoPhotometer® was utilized in this study to quantify DNA by determining its absorbance at 260 nm.
#Implen #NanoPhotometer #UV/VIS #Spectroscopy #InnovationInHealing #BoneRegeneration #ScientificReports #NaturePortfolio #RegenerativeMedicine #GuidedBoneRegeneration #TissueEngineering #DentalInnovation #Biomaterials #MedTech
Breakthrough Natural Membrane for Bone Healing
Healing Nerves with Next-Gen Biotech
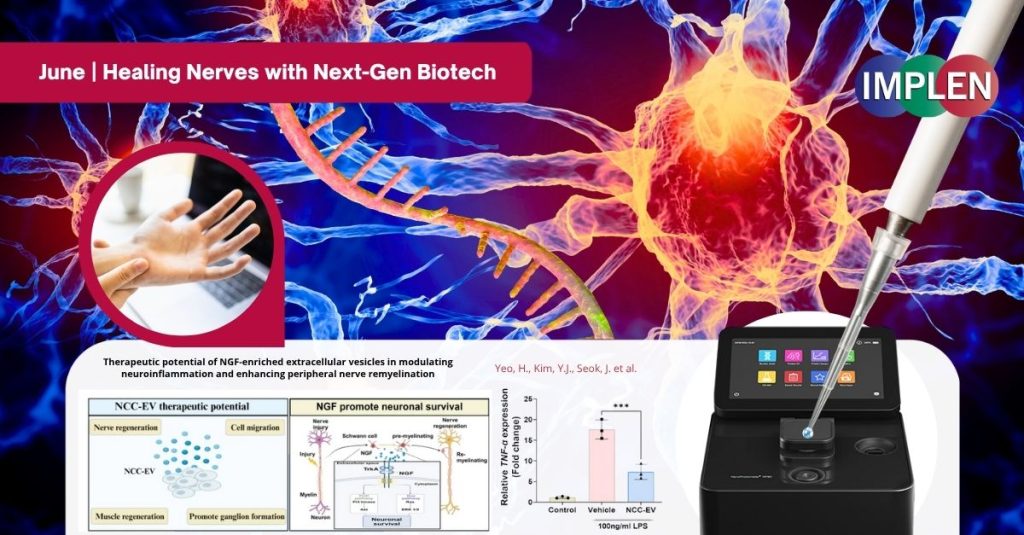
A new study recently published in Acta Neuropathologica Communications showed that extracellular vesicles (EVs) enriched with nerve growth factor (NGF) reduced inflammation, regenerated damaged nerves, and protected muscle in a model of sciatic nerve injury. These NGF-loaded EVs may offer a breakthrough therapy for peripheral nerve injury, with exciting potential to treat neuroinflammation, enhance nerve healing, and support recovery after injury.
The Implen NanoPhotometer® was used in this study to quantify RNA.
#ExtracellularVesicles #NGF #Neurorepair #PeripheralNeuropathy #Neuroinflammation #Implen #NanoPhotometer #Biotech #RegenerativeMedicine #FutureOfHealing
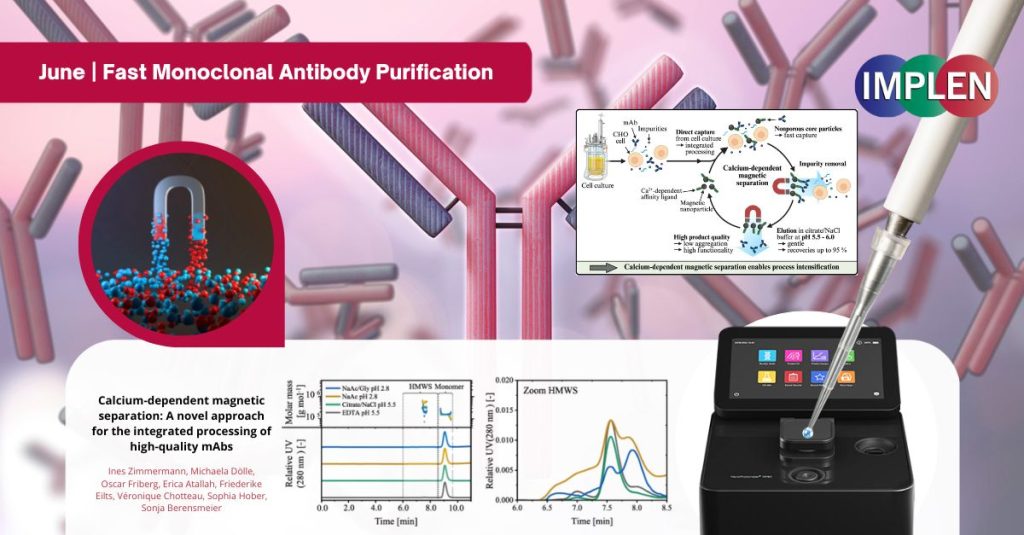
A new study published in Separation and Purification Technology introduced a cleaner, faster way to purify monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) using calcium-dependent magnetic particles. This new method avoided harsh acids, combined cleanup and capture in one step, and worked directly on dense cell cultures—cutting costs, saving time, and preserving antibody quality, providing a promising leap forward for biotech manufacturing.
The Implen NanoPhotometer® was utilized in this study for photometric quantification in kinetic studies to measure the adsorption of pure Trastuzumab to MNP@GPTMS@Z Ca particles as a reference to the adsorption from cell culture. The default settings for human IgG were used.
#Implen #NanoPhotometer #UVVIS #Spectroscopy #BiotechInnovation #MonoclonalAntibodies #MagneticSeparation #CleanBioprocessing #AntibodyPurification #mAbManufacturing #DownstreamProcessing #CalciumDependent #ProteinScience #TUM #KTH #HER2 #Trastuzumab #SustainableBiotech
Revolutionizing Antibody Purification
Unmasking the Role of Sugar Metabolism and Halloween Genes

This issue highlights the work of Gu et al., revealing the critical connection between sugar metabolism and Halloween genes in silkworm development. These genes are essential for producing ecdysteroids, the hormones that drive molting and metamorphosis in insects.
The study demonstrated how the prothoracicotropic hormone (PTTH) activated sugar transporters and trehalase enzymes in the prothoracic glands of silkworms. These enzymes broke down trehalose, a sugar, into glucose, which provided the necessary energy for hormone production. When sugar transport and metabolism were blocked, ecdysteroid levels dropped, showing how vital sugar metabolism is for regulating these hormones.
Interestingly, PTTH selectively enhanced the activity of certain sugar metabolism genes without affecting other key genes involved in glycolysis, the process that breaks down glucose to produce energy. This pointed to a specific role for PTTH in stimulating the sugar-related pathways essential for hormone production. By revealing how PTTH influences both Halloween genes and sugar metabolism, this study sheds light on how hormone production is tightly regulated during insect development. Through this exploration, the research offered new insights into the delicate balance between hormone production and metabolism, deepening our understanding of the complex processes that govern insect growth and development.
The Implen NanoPhotometer® was used in this study to measure RNA concentrations.